(iTers News) - You are watching an action thriller movie on your smart phone, and two spy moles are speeding away along a highway to outrace police officers’ car chasing, swerving to the right and the left, and skidding to a brake. With the whipping and oomphing sound effects, you can feel the real skidding and bumming feel of a car chasing on your hands holding the smart phone as if you are in midst of the real spot.
Not only are smart phones increasingly looking alike in the outer design and shape, but also they are becoming identical on hard performances, as the vast majority of them are running on the Android OS and ARM processor platform.
Life-like haptic experiences
To make differentiation from competition, smart phone makers are innovating on their own user interface, or UI technologies. Called as a tactile feedback technology, haptics is one of the emerging innovative UI technologies that smart phone makers are aggressively implementing on their smart phones, as it can combine with the various sound effects to give users palpable, real world experiences.
With the haptic technology, for example, you can play a virtual guitar app on your smart phone with a palpable touch feel of plucking a real string with your fingers. The applications don’t stop there. It can be used with a wide variety of consumer and industrial applications from smart phones to tablet PCs to mouse wheels to refrigerators to washing machines to microwave ovens.
Two breakthroughs
As more and more innovative applications like AR, or augmented reality apps are going viral, however, smart phone makers are extremely demanding more sensitive and more sophisticated haptic technology. For example, some virtual retailing AR app requires the haptic technology to generate vibrations as close to real touch feel as possible to enable users to even feel as if they bristle with the real fabric of apparels on the store shelves.
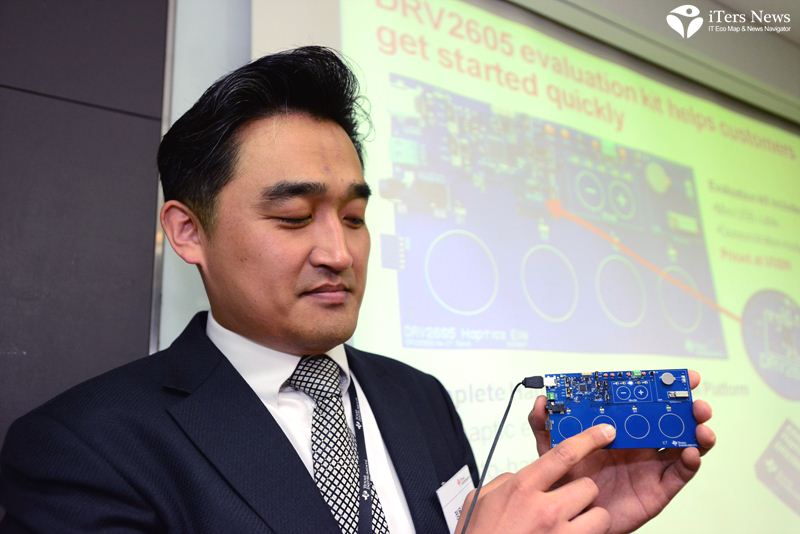
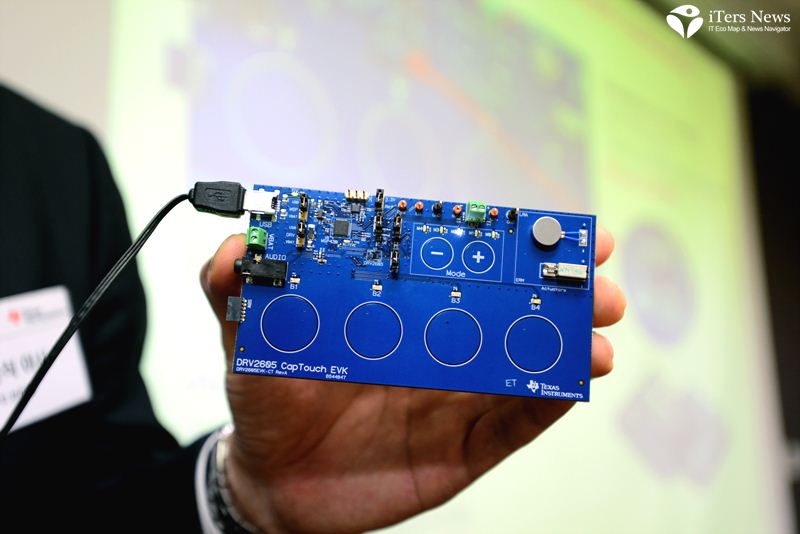
To keep up with the demand, Texas Instruments recently has unveiled a royalty-free haptic driver IC that comes preloaded with a library of 123 distinct haptic effects licensed by tactile feedback software database maker Immersion.
Specifically designed to drive eccentric rotating mass actuator, or ERM and linear resonant actuator, or LRA, the DRV 2605 driver IC comes built with two breakthrough technologies –audio to haptic mode and smart loop architecture.
(Photo caption: Raymond Chung, System Application Manager with TI Korea)
Feel with sound effects
The working theory is straightforward. The whole bunch of haptic system comes complete with a touch screen microcontroller, a haptic driver IC, and a vibration actuator. If smart phone users touch the screen by their hands, for example, the capacitive touch sensor detects the press, and then a built-in MCU senses the touch, pulling the trigger of the DRV2605 haptic driver IC. Then, the driver IC generates an optimal waveform from the library of 123 haptic effects, a firmware of various reference waveforms stored in a ROM circuitry. The waveform revs up the actuator to move in a specific direction or pattern to create a vibration. Usually, there are three types of actuators – piezo motor, EBM, and LRA.
The library of haptic effects is a collection of digitalized reference waveforms that have been sampled from genuine analog waveforms of real physical world.
Auto resonance
What makes the DRV2605 driver IC from other rival products is that it has a wealthy library of royalty-free 123 reference waveforms that can create tons of haptic effects on a wide variety of devices, as TI already licensed them from Immersion, Inc.
“The library is so rich that it can generate up to 123 haptic vibration effects,” said Raymond Chung, system application manager, strategic solutions, audio imaging products with TI Korea, Ltd.
When smart phone users slightly tap into the virtual water well app on their smart phone with their finger, for example, he showed in his demo how vividly the haptic water ripple effects were being felt across smart phone users’ hands as if they submerge their fingertip into a real fountain.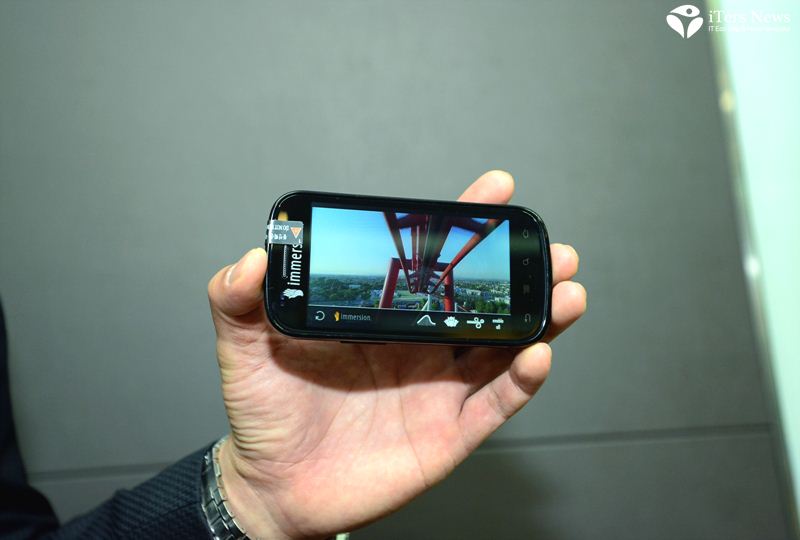
Its smart loop architecture is another technology breakthrough that makes the driver IC stick out from competition, featuring auto-resonance, or auto-calibration capability.
Track optimal resonance frequency
As time goes by, the originally preset working resonance frequency range of the actuator gradually starts to deteriorate by a slight margin, resulting in the loss in the vibration power of the actuator. The built-in auto-resonance, or auto-calibration algorithm works to keep track of the changes in the resonance frequency and automatically fine-tune it to maximize the vibration effects of the actuator as powerful as the preset-mode. It also can help reduce start-up and braking time of the actuators. The technology breakthrough translates into two times vibration power, enables it to operate half at the power consumption of competing solution.
The DRV2605 works with any of TI’s touch screen controller family, and is now available in a 9-ball, 1.5-mm by 1.5-mm by 0.6-mm WCSP package.
Videos & Photos by JH Bae