Built with dozens of vision and radar sensors and MCUs, they are so smart that they see around themselves not only to warn of lane departures and near-collisions with cars ahead, but also help drivers to park them safely in the blind spots.
They also feature smart phone-like driver-friendly UIs, or user interfaces that can allow drivers to remotely control car door and window systems as well as a car engine ignition system. But the NFC-based key-less system can also identify car owners and say hello when they approach their cars.
Coming built with sensors and algorithms for natural human languages, cars can even interact with drivers with a command of voice.
As car makers and other IT technology giants like Google and Apple are now jockeying in the race to build self-driving cars, cars of tomorrow will likely come embedded with more of chips and software algorithm like AI, or artificial intelligence.
By 2018, for example, cars of the future will come connected with each other or road infrastructures to get aware of neighboring environments and talk with them, or cars in the vicinity to think, judge and act in the way that they are supposed to do to avoid collision, or park safely.

Lars Reger
NXP Automotive CTO
Yet, the automotive chip market isn't as big as those for smart phones and PCs in terms of unit shipments.
To address such market that requires myriad of chips, but in not so big volume, consolidation is a key. Not only will it give economies of scales, but also allow chip makers to make their chip portfolio rich enough to meet enormously diverse product requirements. The consolidation also helps them save costs and time in the research and development projects.
NXP Semiconductors proves that a winning strategy, as it completed its merger of with Freescale Semiconductor on Dec 7, 2015.
The marriage remakes NXP as the world's No. 4 chip maker with more than US$ 10 billion in annual revenue.
When it comes to automotive market, the newly reborn NXP Semiconductors is an undisputed No. 1 chip maker in the world, claiming over US$3 billion in annual revenue, shipping about 40% to 45% of the chip production in the automotive market. .
No chip makers are today as rich as NXP Semiconductors in their chip portfolio for automotive applications.
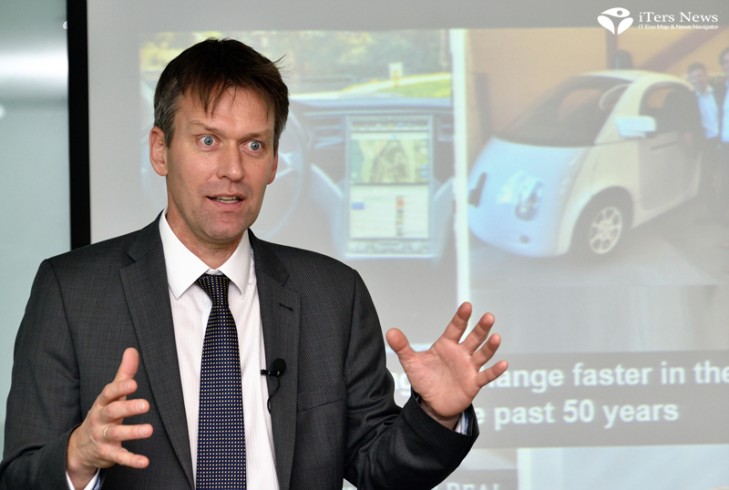
Self-driving robots
“The industry is more and more moving talking about robots. If we are looking into the automotive market from IT perspective, (we have challenges) of how w can reconstruct self-driving robots. If you are looking from that angle, you have to have IT discussion –how to build best IT system and how to build best robots. NXP has everything in place to build a complete set of self-driving robots. We have nothing missing in our portfolio, said Lars Reger, vice president and CTO with NXP automotive business units.
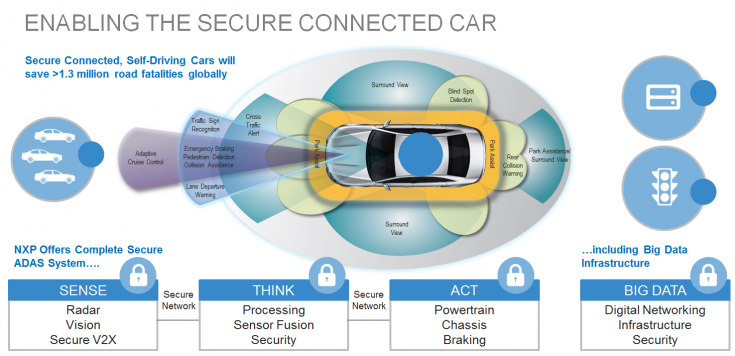
Its recently released radar sensor module is a testimony to how the merger with Freescale has enabled NXP to better address automotive market. The module is one piece of the technology building blocks that NXP is now trying to piece together to help car makers to deliver on their vision on self-driving cars.
Optimized for ADAS, or advance driver assistant system, the 3x3cm module comes built with NXP’s RF CMOS front-end radar radio chip and Freescale’s radar microcontroller.
On the other side of the module are NXP’s Ethernet networking ICs and Freescale’s power management ICs.
“If you look at the radar sensor module, now we can understand the capability of the two companies’ merging, because we have a perfect fit for RF front-end electronics and radar microcontrollers,” added CTO Lars Reger.
The module has 4 receiver antennas and 3 transmitter antennas. The RF CMOS front-end radar chip is a highly integrated radar RF transceiver chip that integrates a transmitter, a receiver, a signal generator and other ADC, or analog to digital converter chip on a single piece of silicon. Compared with previous bulky silicon germanium, or SiG front-end radar chip, it is a lot more power-efficient, just consuming 40% less power.
According to NXP, Google has been using this radar sensor chip for Google cars.
World’s first CMOS front-end RF radar chip
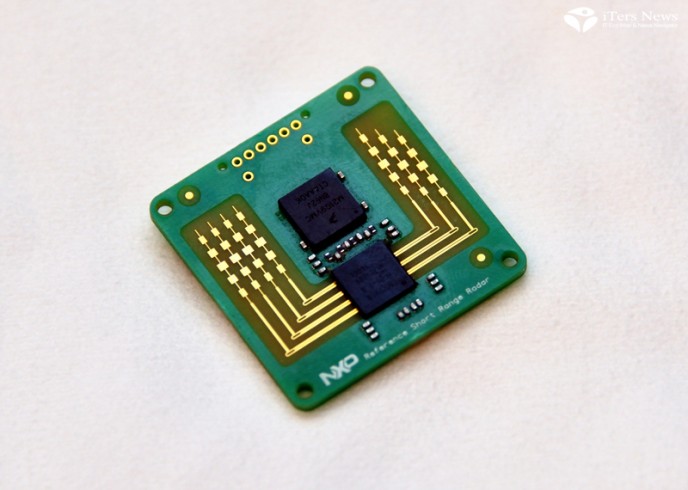
The chip is the world’s first front-end RF radar chip solution that is fabricated with low-power CMOS chip-making process.
The implementation of front-end RF radar radio in the CMOS process will ultimately allow NXP to combine the radar sensor block and MCU block in a single chip, as MCUs are most fabricated with CMOS process. A short for complementary metal oxide semiconductor, the CMOS is a sort of low-power chip-making process that combines N type transistors and P type transistors in a complementary way.
CMOS process is a plain vanilla technology to fabricate MCUs,“ says CTO Lars Reger.
Vision-based camera sensors for ADAS and MCUs are Freescale's lasting legacies, too. Especially, microcontroller and microprocessor product line ups were major allures that drove NXP to merge with Freescale, as they were the centerpiece of NXP's long-term strategy to remake itself as a jack of all trades for self-driving car market.
Take for example, Freescale’s high-end computational monster microprocessor for cloud computing. Comes built with 12 to 20 processor cores, the microprocessor chip will be able to work its way as a brain for future-proof self-driving cars, processing various sensing signals and then calculating them to order how self-driving cars should behave.

Lars Reger
NXP ¹ÝµµÃ¼ ¿ÀÅä¸ðƼ ºÎ¹® ºÎ»çÀå °â CTO
12 to 20 core computational monster
“What we are doing with that? If you take the 12 core microprocessor for example, you are 4 cores, and you are a watchdog. You are checking that the system is all alive, which is important for the functional safety. The other 8 cores , they are doing what’s called as a sensor fusion. They are getting all the signals from radar sensors, camera sensors, car to car communications system, and telematics, calculating one driving advice out of that and calculating how autonomous driving car should behave,“ stressed CTO Lars Roger.
According to him, the self-driving cars of tomorrow will behave like robots. Like robots, for example, the self-driving cars get as much information as possible about neighboring environments via its built-in radar systems, vision-based cameras, car to car communications system. And, MCU-based sensor fusion works as human brain to think and send driving advices to activate various actuators like a power train, a steering wheel, and a braking system.
Car to car, or vehicle to infrastructure communications system are central part of the self-driving car system, too.
NXP has been testing the IEEE 802.11p based-Roadlink V2X system with car makers and other system integrators as well as service providers. There are my usage scenarios. Coming first is the platooning service of cargo trucks, under which cargo trucks on the platoon form an IEEE802.11p Wi-Fi network to communicate with each other to synchronize their driving wirelessly.
In the usage case, which is now put to commercial test, a lead cargo truck blazes the trail wireless synchronizing the movements of other car trucks on the V2X network as if a locomotive pull in other passenger compartment cars. The V2X chip will hit roads in 2017, GM is working with Delphi to implement it on the GM brand car.
Ethernet carries power and signals
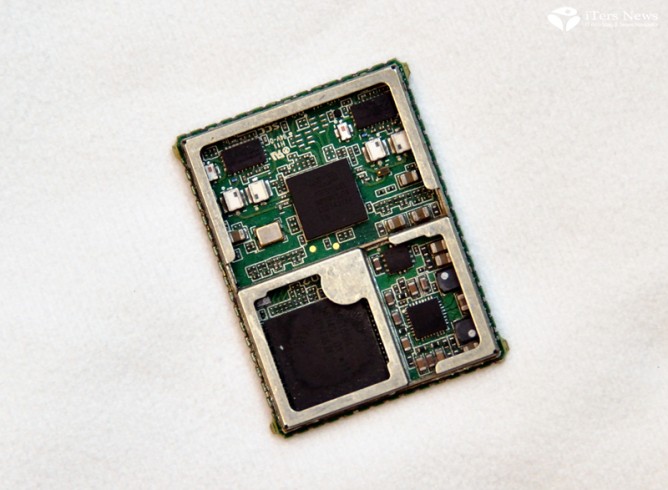
NXP is also market leader in the in-vehicle networking businesses like CAN, LIN, and, FLEXRAY. Especially, the chip maker is now producing Ethernet PHY in high volume. Ethernet technology can carry signals as well as power, allowing car makers to take out power cables and thus save costs and weights
Called as crypto-controller, NXP’s unbreakable secure element chip is what makes NXP stand out from competition, as hackers are trying to break the car communications system. That legacy crypto-controller chip is the same sort of chip that has been used in consumer applications like passport ID chips. The secure element security chips can be implemented into car to car communications, systems, ADAS and telematics systems to protect the system from hacking attempts.
For car infotainment system, the chip maker has all silicon contents to build the whole bunch of system from man to machine interfaces, graphics interfaces, high-end premium radios, including software-defined radio chips and intelligent power amplifiers. About 19 of the top 20 car radio makers use NXP’s radio chips.
For example, NXP will soon tape out a thumbnail-sized one single radio chip solution that incorporates everything from AM/FM radio, software-defined digital radio, TVs, 6 tuners and intelligent amplifiers. Due out two weeks, the chip is the world’s single radio chip solution that combines two chip solution - AM/RM radio and software-defined digital radio chips - in a single piece of silicon chip.


Ucode_RF ID

